The UAE is dynamic in digital business, and with the emergence of businesses agglomerated in data, data protection is coming into the fore front. The UAE has reacted by implementing the Personal Data Protection Law PDPL that took effect on June 2, 2020. The law defines how personal data can be collected, processed, and stored, how the rights of individuals are guaranteed, and it puts an obligation on businesses and organizations in which such data.
In this blog, I aim to guide you through the main aspects of Data Protection Law in UAE, its requirements and how this affects businesses and individuals.
Personal Data Protection Law in The UAE
The PDPL is the backbone of regulatory developments in the area of data privacy in the UAE, and the purpose of this regulation is to create a legal mechanism for protecting the personal data of individuals. It will cover both the publicly-owned and privately-owned business that handles personal data in the country and guarantee the protection of personal information, build trust in the digital economy, and be consistent with international standards of data protection.
Scope of the PDPL
The PDPL applies to any processing of personal data that occurs within the UAE. This includes:
- Data Controllers and Processors: Data is controlled or handled by parties that are inside or outside the UAE, but as long as the data involves residents or citizens of UAE, the law still applies.
- Cross-Border Applicability: The law is likewise to be applicable when a data controller or a data processor is not in the UAE, though processing the personal information of individuals in the UAE.
Key Definitions Under the PDPL
As part of compliance, it is crucial to understand the core terminology. The PDPL gives key terms, which are defined, including:
- Personal Data: any data that concerns an identified or identifiable person. This is all name, ID numbers, location, and online identifiers, etc.
- Data Controller: Is the party that decides the means and purposes of processing personal information.
- Data Processor: The entity that processes personal data on behalf of the data controller.
- Sensitive Personal Data: Data about issues of race or health and biometric data (finance or crimes).
- Processing: An action carried out to personal any data, including collection, storing, use, and sharing.
Data Controller and Processor Responsibility
With the PDPL, regardless of whether one is a data controller or a data processor, he or she has vital obligations towards keeping personal data in check. These responsibilities are meant to protect the right of privacy of people and ensure the transparency of data processing.
1. Obtaining Explicit Consent
The data controllers and processors have to establish explicit and informed consent of the individuals before they can collect or process their data. This means:
- Transparency: It is your responsibility as a business to indicate why you need the data, how you intend to utilize the data, and the rights of individuals regarding their data.
- Revocable Consent: The individuals can withdraw his/her consent at will.
2. Legitimacy, Justice, and Openness
The PDPL underlines that processing of personal data shall be:
- Legal: On a legally acceptable standing.
- Fair: Is performed in a non-misleading manner.
- Transparency: Individuals should be told the purposes of the processing.
3. Technical/Organization Measures
To ensure the security of personal data, controllers and processors are expected to implement the technical and organizational measures. This includes:
- Data Encryption: Coding of personal data to keep off gate crashers.
- Access Controls: Putting the personal data behind measures limiting access to it to authorized individuals.
- Data Minimization: Data is minimized by not collecting more than is needed to achieve their purpose.
4. Data Breach Notifications
In case of a data breach that may affect the personal data, organizations will be required to:
- Inform affected persons: Timely inform affected persons about the breach affected persons.
- Report to Data Protection Authority (DPA): Report to the DPA without any unnecessary delay and inform them of the details of the breach and rectification.
Special Provisions for Sensitive Personal Data
The PDPL provides additional protection to sensitive personal data, e.g., biometric, health, and financial information. The processing of such data requires stricter conditions:
1. Additional Safeguards
Processing sensitive data is the reason why it requires more measures, which include:
- Explicit Consent: You are required to seek the express consent of the person before you process his/her sensitive data.
- Security Measures: Install more security measures to guard sensitive data against being accessed or revealed to those who have no access rights.
2. Limited Processing
Sensitive personal data is only processable in certain situations, like:
- Vital Interest: Processing is obligatory as it is needed to defend the life or vital interests of the person.
- Laws: Processing may be necessary to meet the requirements of a law.
Data Transfer over Borders
The PDPL also deals with data transfer to countries beyond the UAE since companies tend to have international operations. The PDPL will ensure that the data transferred does not lack protection.
1. Sufficient data security in the recipient country
Personal data may be exported elsewhere when the relevant recipient country has commensurable data protection laws similar to the PDPL. Before the transfer of data, you must make sure that:
- The recipient country has similar or stronger data protection laws.
- The transfer complies with the provisions of the UAE Data Protection Authority (DPA).
2. Protections to Non-Adequate Countries
Where the recipient country lacks sufficient measures, data controllers are required to insert extra safeguards, including:
- Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs): Binding Contractual clauses, assuring the protection of data.
- Mechanisms of Certification: Certification of conformity in the UAE regarding data protection requirements.
3. Data Portability
People can demand that their data be transmitted by one data controller to another, which is referred to as data portability. You must facilitate the transfer in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format.
Rights of Individuals Under the PDPL
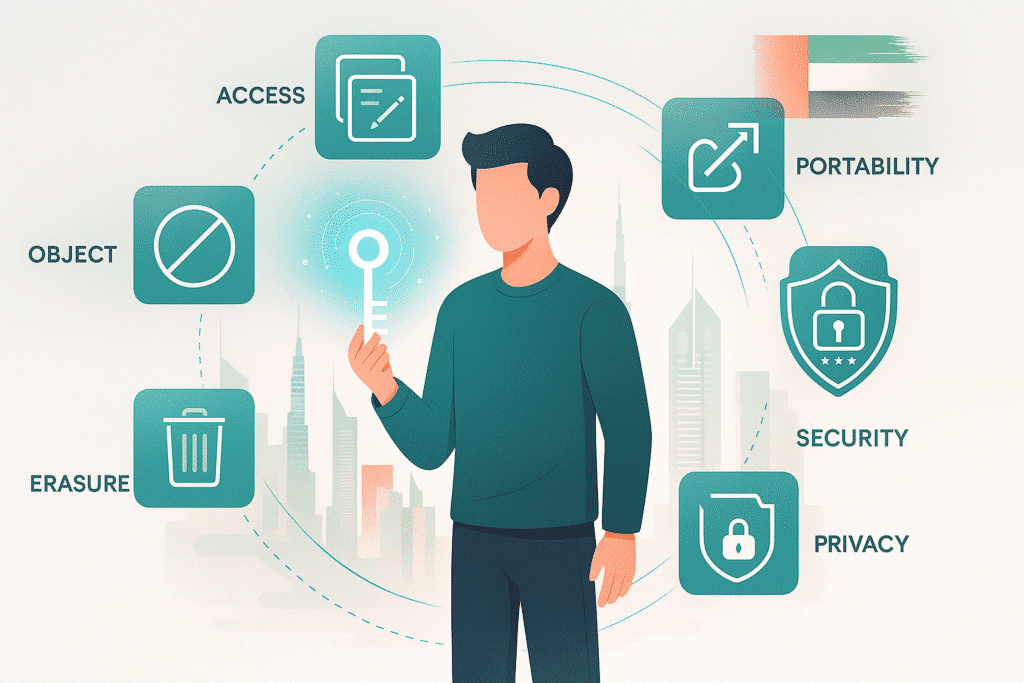
The PDPL has various rights on individuals on how their data is to be processed. These rights give the users control over their data and its use.
1. Right to Access
Patients are entitled to access their data and to demand information about the way it is used. As a business, you must provide:
- Copy of data: With a request, a person should be provided with a copy of his/her data.
- Information on the processing activities: The purpose, basis, and recipients of the information must also be informed.
2. Right to Rectification
Individuals may demand the corrections or updating of their information in case it is faulty or incomplete. You must:
- Respond Promptly: Make the necessary changes without undue delay.
3. Right to Object
One can complain about the fact that his data is processed in the case when:
- Direct Marketing: They can opt out in case they do not agree to the marketing communications.
- Automated Decision-Making: When solely by automated processing, decisions have been made that impact their lives, people can object.
4. Right to erasure (right to be forgotten)
People can demand the deletion of their information in case it is no longer needed as per the purposes of its gathering. You must:
- Erase the Data: Delete the personal data without any undue delay when asked to do so, unless there may be a legal obligation that exists to prevent this deletion.
5. Right to Data Portability
Users are entitled to access their information in a structured format and transfer it to another controller to the extent that they wish. Such a right is essential to those people who want to change their service provider.
Implementation and Fees
UAE Data Protection Authority (DPA) is the regulatory entity charged with the implementation of the PDPL. It can:
1. Investigate Complaints
The DPA can investigate complaints lodged by individuals concerning data protection violations. It may:
- Conduct Audits: Conduct inspections and audits in order to verify conformity with the law.
- Request Information: Require businesses to provide documentation related to their data processing activities.
2. Impose Penalties
Failure to comply with the PDPL may result in great penalties, which include:
- Fines: Businesses that do not adhere to the stipulations of the PDPL could attract fines for such enterprises.
- Corrective Measures: The DPA can impose corrective measures on organizations to address data protection contraventions.
Additional Considerations Under the PDPL
1. Data Retention
The PDPL is silent as to a general data retention period; data controllers are required to keep personal data as long as reasonably needed to achieve particular purposes by collecting their data. You should:
- Retention Policies: Personal information must be retained only as long as is necessary, and after that, it must be securely destroyed.
2. International Cooperation
The PDPL also facilitates international collaboration with foreign data protection authorities to handle cross-border data protection behaviors. This makes businesses with cross-border operations conform to international standards.
FAQs:
What is the UAE PDPL?
The Personal Data Protection Law PDPL is the law governing the collection, storage, and processing of personal data in the UAE by businesses and government organizations.
Who does the PDPL apply to?
It applies to all organizations inside the UAE and even foreign companies if they process data of UAE residents.
What are individual rights in the PDPL?
You may access, correct, delete, transfer, or object to the use of your data in some cases.
What are the incursions of non-compliance?
Non-compliant businesses may be hit with heavy fines, corrective actions by the UAE Data Protection Authority.
Final Words
PDPL in the UAE is a step towards implementing the security of personal data of individuals and regulating its use in businesses. You, as a reader, can be assured that your personal information is under a protective legislative arsenal. In business, the PDPL should be a requirement to prevent penalties and to develop trust with business partners. The legislation promotes transparency, accountability, and safety in the virtual sphere, which makes it one of the important elements of an effective economy in the UAE.

